Half-Normal Probability Plot: Difference between revisions
imported>Donal (Created page with "The following describes the Half-Normal Probability plot for analyzing Design of Experiments results with MLR. ===Half-Normal Plot=== Half-Normal plots are used to iden...") |
imported>Donal No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
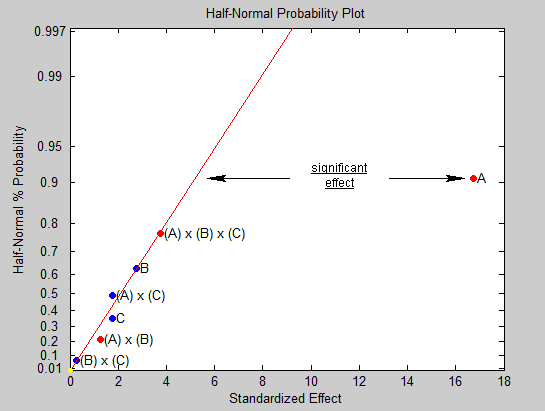
Half-Normal plots are used to identify which experiment factors have important effects on the response. Clicking on the 'Half-Norm' menu button will open a Half-Normal probability plot. | Half-Normal plots are used to identify which experiment factors have important effects on the response. Clicking on the 'Half-Norm' menu button will open a Half-Normal probability plot. | ||
[[Image:Halfnormplot.png]] | |||
This plot shows the magnitude of the experiment's effects as “Standardized Effects”, ordered in increasing magnitude, along the x-axis. The y-values are given by the idealized expected values for this number of effects if they were drawn from a half-normal distribution. A half-normal distribution is the distribution of the abs(X) with X having a normal distribution with mean zero. | This plot shows the magnitude of the experiment's effects as “Standardized Effects”, ordered in increasing magnitude, along the x-axis. The y-values are given by the idealized expected values for this number of effects if they were drawn from a half-normal distribution. A half-normal distribution is the distribution of the abs(X) with X having a normal distribution with mean zero. | ||
Revision as of 16:20, 7 November 2011
The following describes the Half-Normal Probability plot for analyzing Design of Experiments results with MLR.
Half-Normal Plot
Half-Normal plots are used to identify which experiment factors have important effects on the response. Clicking on the 'Half-Norm' menu button will open a Half-Normal probability plot.
This plot shows the magnitude of the experiment's effects as “Standardized Effects”, ordered in increasing magnitude, along the x-axis. The y-values are given by the idealized expected values for this number of effects if they were drawn from a half-normal distribution. A half-normal distribution is the distribution of the abs(X) with X having a normal distribution with mean zero.
The plot contains a straight red line which is drawn through the expected values of N effects if all of the effects are small. Factors having small effects will be plotted near the plot’s straight red line. Factors having large effects will be plotted farther to the right, and this is how important effects are identified in the Half-Normal plot. Factor A is likely to be an important effect for the DOE shown in the figure below because its data point lies well off the straight red line. The other effects are likely to have unimportant effects since they lie close to the red line.
For a full discussion of Half-normal Probability plots see
http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/pri/section5/pri598.htm