Loading and Saving: Difference between revisions
imported>Jeremy No edit summary |
imported>Jeremy No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Loading From the Workspace and MAT Files== | ==Loading From the Workspace and MAT Files== | ||
Solo and PLS_Toolbox save in the native MATLAB binary file format. This format is compact and quick to read and write, but is, obviously, not compatible with other programs necessarily. | Solo and PLS_Toolbox save in the native MATLAB binary file format called a MAT file. This format is compact and quick to read and write, but is, obviously, not compatible with other programs necessarily. There are also a number of options to Import and Export data and models to other formats. | ||
Solo and PLS_Toolbox also make use of a "workspace" which is a memory-only space to store data, models and other objects. This workspace only exists when the program is running and will be cleared when the program is exited. | |||
Load and Save operations to either MAT files or the Workspace use a common interface. This interface can be used to switch between workspace and file modes using the button located in the lower left corner. The Workspace view allows you to save or load directly to/from the current Workspace; The File view allows you to save or load directly to/from a .mat file. | |||
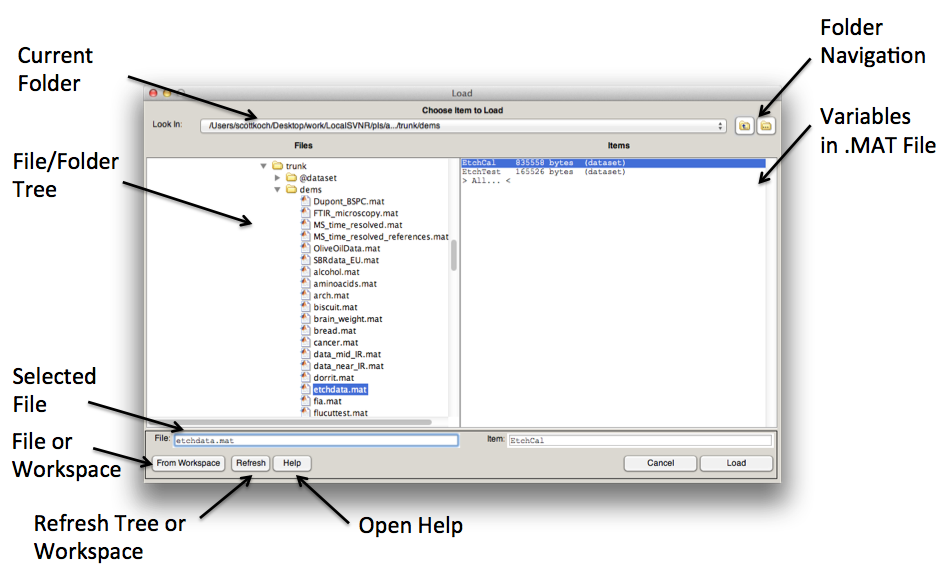
Load | |||
In File view, the controls at the top of the window allow for standard folder navigation. The two list boxes, Files and Variables, show, respectively, the available files in the currently selected folder and the available variables in the currently selected .mat file. Note that a .mat file can contain several variables and you can select one or more from the Variables list to load. When saving to a .mat file you must name both the file and the variable (i.e., both the File and Variable text boxes must have values in them). Also notice that in the Files list a name preceded with “[ ]” indicates a folder. To navigate into any folder, either double-click the folder name in the listbox or select it and click the Open button. | In File view, the controls at the top of the window allow for standard folder navigation. The two list boxes, Files and Variables, show, respectively, the available files in the currently selected folder and the available variables in the currently selected .mat file. Note that a .mat file can contain several variables and you can select one or more from the Variables list to load. When saving to a .mat file you must name both the file and the variable (i.e., both the File and Variable text boxes must have values in them). Also notice that in the Files list a name preceded with “[ ]” indicates a folder. To navigate into any folder, either double-click the folder name in the listbox or select it and click the Open button. | ||
| Line 32: | Line 31: | ||
==Saving Models and Data== | ==Saving Models and Data== | ||
Save/Export functionality can be found in the '''File''' menu. All data objects (datasets, models, and predictions) can be saved in .mat files | Save/Export functionality can be found in the '''File''' menu. All data objects (datasets, models, and predictions) can be saved in .mat files or exported to CSV or XML from the '''File''' menu of the DataSet Editor. Models can be exported as XML or m-files from the '''File''' menu in Analysis as well as several other formats (depending on the model type and purchased program options) | ||
Revision as of 14:38, 7 October 2008
Loading From the Workspace and MAT Files
Solo and PLS_Toolbox save in the native MATLAB binary file format called a MAT file. This format is compact and quick to read and write, but is, obviously, not compatible with other programs necessarily. There are also a number of options to Import and Export data and models to other formats.
Solo and PLS_Toolbox also make use of a "workspace" which is a memory-only space to store data, models and other objects. This workspace only exists when the program is running and will be cleared when the program is exited.
Load and Save operations to either MAT files or the Workspace use a common interface. This interface can be used to switch between workspace and file modes using the button located in the lower left corner. The Workspace view allows you to save or load directly to/from the current Workspace; The File view allows you to save or load directly to/from a .mat file.
In File view, the controls at the top of the window allow for standard folder navigation. The two list boxes, Files and Variables, show, respectively, the available files in the currently selected folder and the available variables in the currently selected .mat file. Note that a .mat file can contain several variables and you can select one or more from the Variables list to load. When saving to a .mat file you must name both the file and the variable (i.e., both the File and Variable text boxes must have values in them). Also notice that in the Files list a name preceded with “[ ]” indicates a folder. To navigate into any folder, either double-click the folder name in the listbox or select it and click the Open button.
Importing From Other Sources
Data can be imported from a variety of sources using File>Import Data. Sources include:
- Workspace/MAT file
- Delimited Text File (CSV,TXT)
- XY... Delimited Text Files (TXT,XY)
- Excel File (XLS,CSV,TXT)
- Hamilton Sundstrand ASF File (ASF, AIF, BKH)
- Thermo Galactic File (SPC)
- JCAMP [general] (DX,JDX)
- Extensible Markup Language (XML)
- Paste XML from Clipboard
In some cases you may have to use the DataSet Editor to add additional information to your Dataset. For instance, you may add labels and or axis scales after you've imported the raw data. See Key_GUIs for more information on using the DataSet Editor.
In cases involving n-way (multidimensional) data you man need to "build up" you dataset. More information about how to do that can be cound here.
Saving Models and Data
Save/Export functionality can be found in the File menu. All data objects (datasets, models, and predictions) can be saved in .mat files or exported to CSV or XML from the File menu of the DataSet Editor. Models can be exported as XML or m-files from the File menu in Analysis as well as several other formats (depending on the model type and purchased program options)