Evri release management: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
EVRI release management process includes the following: | EVRI release management process includes the following: | ||
* Continuous development - EVRI staff all work from the latest version of products so any changes are immediately tested in real world use. Typically a staff member will update from the repository at the beginning of work day. Note, occasionally staff will work from an existing release to maintain version compatibility with a customer. | * Continuous development - EVRI staff all work from the latest version of products so any changes are immediately tested in real world use. Typically a staff member will update from the repository at the beginning of a work day. Note, occasionally staff will work from an existing release to maintain version compatibility with a customer. | ||
* Version Control - EVRI maintains modern version control software and processes to manage software development. | * Version Control - EVRI maintains modern version control software and processes to manage software development. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
** Model [[Standard_Model_Structure#model.detail|detail.history]] field contains an entry log of datetime and changes made to the model. | ** Model [[Standard_Model_Structure#model.detail|detail.history]] field contains an entry log of datetime and changes made to the model. | ||
** DataSet [[DataSet_Object_Fields#.history|.history]] field contains a running history of commands that have modified the DataSet contents. | ** DataSet [[DataSet_Object_Fields#.history|.history]] field contains a running history of commands that have modified the DataSet contents. | ||
** The [[Analysis_Window:_Model_Cache_Pane|Modelcache]] stores models and data upon calculation in the analysis interface. The model cache interface keeps a | ** The [[Analysis_Window:_Model_Cache_Pane|Modelcache]] stores models and data upon calculation in the analysis interface. The model cache interface keeps a history of calculated models. Note, settings for managing history (max age and size) will impact exactly what is tracked. See [[Analysis_Window:_Model_Cache_Pane|documentation]] for more information. | ||
== Model Validation Information == | == Model Validation Information == | ||
It is recommended that customers develop a model within Solo/PLS_Toolbox as COTS (commercial off-the shelf) software. Then validate the model to their own standards paying special attention to how a model performs with previously unused data that spans the range of the samples you expect the model to work with. | It is recommended that customers develop a model within Solo/PLS_Toolbox as COTS (commercial off-the shelf) software. Then validate the model to their own standards paying special attention to how a model performs with previously unused data that spans the range of the samples you expect the model to work with. | ||
'''NOTE: The following steps are still under development.''' | |||
Steps to consider when validating a model: | |||
* Does your calibration data span the variation you expect from your system. | |||
* Are you holding out sufficient data to validate your model against. | |||
* Do you have a plan for maintaining your model. | |||
Latest revision as of 12:57, 12 February 2021
Eigenvector Research Inc. follows industry standards for software production. EVRI release management process includes the following:
Release Management
EVRI release management process includes the following:
- Continuous development - EVRI staff all work from the latest version of products so any changes are immediately tested in real world use. Typically a staff member will update from the repository at the beginning of a work day. Note, occasionally staff will work from an existing release to maintain version compatibility with a customer.
- Version Control - EVRI maintains modern version control software and processes to manage software development.
- Issue Tracking - A software project management system for bug and enhancement tracking is used to document and manage software development.
- Testing - A mix of manual and automated testing is conducted to verify product quality. Each major release is regression tested to prior releases to assess numeric consistency.
- Release Notes - All significant changes and known issues are documented in the release notes.
Installation and Tracing Information
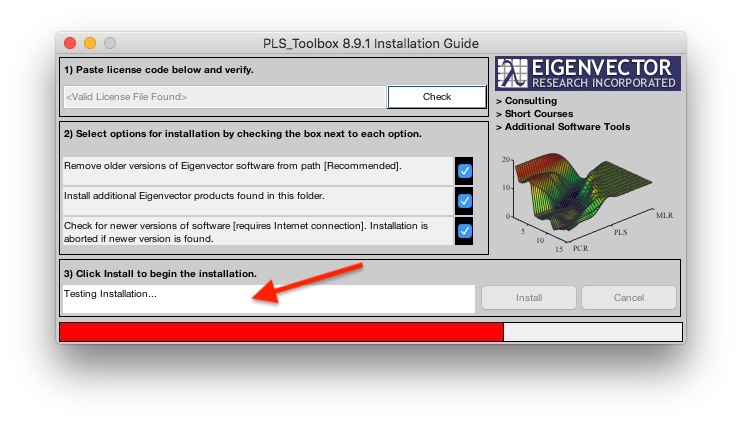
- All software is tested for common errors at the time of installation. A message appears in the installation window indicating the tests are being run. If an issue is encountered a warning dialog box will appear, otherwise the installation will proceed to open the main window.
- Solo and PLS_Toolbox have some tools to help trace model development but these are not a part of a certified regulatory environment. Tracing model development can be done using the following functionality:
- Model detail.history field contains an entry log of datetime and changes made to the model.
- DataSet .history field contains a running history of commands that have modified the DataSet contents.
- The Modelcache stores models and data upon calculation in the analysis interface. The model cache interface keeps a history of calculated models. Note, settings for managing history (max age and size) will impact exactly what is tracked. See documentation for more information.
Model Validation Information
It is recommended that customers develop a model within Solo/PLS_Toolbox as COTS (commercial off-the shelf) software. Then validate the model to their own standards paying special attention to how a model performs with previously unused data that spans the range of the samples you expect the model to work with.
NOTE: The following steps are still under development.
Steps to consider when validating a model:
- Does your calibration data span the variation you expect from your system.
- Are you holding out sufficient data to validate your model against.
- Do you have a plan for maintaining your model.