Workspace Browser: Data Icons 2: Difference between revisions
imported>Jeremy No edit summary |
imported>Jeremy |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
[[TableOfContents|Table of Contents]] | [[WorkspaceBrowser_DataIcons|Previous]] | [[DataSetEditorWindow_Layout|Next]] | [[TableOfContents|Table of Contents]] | [[WorkspaceBrowser_DataIcons|Previous]] | [[DataSetEditorWindow_Layout|Next]] | ||
| Line 6: | Line 7: | ||
After you have imported or loaded data items into the Workspace Browser, a variety of options are available for manipulating the item, including: | After you have imported or loaded data items into the Workspace Browser, a variety of options are available for manipulating the item, including: | ||
* [[#Viewing information about the item|Viewing information about the item]] | |||
* [[#Opening the item for viewing or editing|Opening the item for viewing or editing]] | |||
* [[#Dragging and dropping items|Dragging and dropping items]] | |||
====Viewing information about the item==== | ====Viewing information about the item==== | ||
| Line 29: | Line 16: | ||
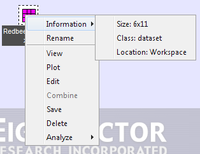
You can right-click on an icon and on the context menu that opens, select from options for viewing information about the item, renaming the item, and viewing details about the item. For a data item, options are also available for plotting the imported data, editing the item, and analyzing the data. In addition, if multiple data items are selected, then an option to combine the data items is also available. | You can right-click on an icon and on the context menu that opens, select from options for viewing information about the item, renaming the item, and viewing details about the item. For a data item, options are also available for plotting the imported data, editing the item, and analyzing the data. In addition, if multiple data items are selected, then an option to combine the data items is also available. | ||
''Context menu for an item in the Workspace Browser'' | :''Context menu for an item in the Workspace Browser'' | ||
[[Image:Imported_data_context_menu.png|200x154px]] | ::[[Image:Imported_data_context_menu.png|200x154px]] | ||
:: | |||
====Opening the item for viewing or editing==== | ====Opening the item for viewing or editing==== | ||
| Line 37: | Line 25: | ||
Double-click an icon to open the item for viewing only or for editing. | Double-click an icon to open the item for viewing only or for editing. | ||
{| | {| | ||
|- | |- valign="top" | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 46: | Line 34: | ||
|} | |} | ||
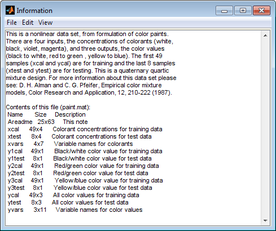
''Information dialog box'' | :''Information dialog box'' | ||
[[Image:Information_dialog_box_view_only_item.png|276x231px]] | ::[[Image:Information_dialog_box_view_only_item.png|276x231px]] | ||
:: | |||
{| | {| | ||
|- | |- valign="top" | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 59: | Line 48: | ||
|} | |} | ||
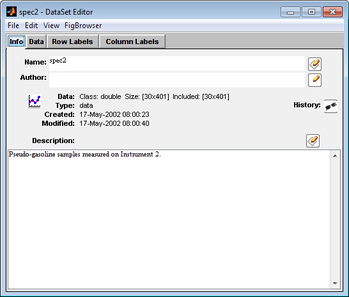
''DataSet Editor window'' | :''DataSet Editor window'' | ||
[[Image:Dataset_editor_window.png|349x297px]] | ::[[Image:Dataset_editor_window.png|349x297px]] | ||
:: | |||
{| | {| | ||
|- | |- valign="top" | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 72: | Line 62: | ||
|} | |} | ||
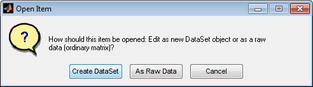
''Open Item dialog box'' | :''Open Item dialog box'' | ||
[[Image:Open_Variable_dialog_box.png|314x87px]] | ::[[Image:Open_Variable_dialog_box.png|314x87px]] | ||
:: | |||
Because, in general, any data that is loaded into Solo must ultimately be converted to a DataSet object, you can click Create Dataset to proactively carry out this conversion; otherwise, you can click As Raw Data to edit the item "as is." The same window opens whether you click Create DataSet or As Raw Data; however, as shown in the figure below, if you click Create DataSet, all of the tabs are enabled for the Dataset Editor window while if you click As Raw Data, only the Data tab is open for the Data Editor window. | Because, in general, any data that is loaded into Solo must ultimately be converted to a DataSet object, you can click Create Dataset to proactively carry out this conversion; otherwise, you can click As Raw Data to edit the item "as is." The same window opens whether you click Create DataSet or As Raw Data; however, as shown in the figure below, if you click Create DataSet, all of the tabs are enabled for the Dataset Editor window while if you click As Raw Data, only the Data tab is open for the Data Editor window. | ||
''DataSet Editor window and Data Editor window'' | :''DataSet Editor window and Data Editor window'' | ||
[[Image:WorkspaceBrowser_DataIcons_2.09.1.5.jpg|533x223px]] | ::[[Image:WorkspaceBrowser_DataIcons_2.09.1.5.jpg|533x223px]] | ||
:: | |||
With some exceptions, if you edit a data item, you must explicitly request to overwrite the data item in the Workspace Browser with the changes. To save changes to a data item: | With some exceptions, if you edit a data item, you must explicitly request to overwrite the data item in the Workspace Browser with the changes. To save changes to a data item: | ||
{| | {| | ||
|- | |- valign="top" | ||
|1. | |1. | ||
| Line 96: | Line 88: | ||
:The Save dialog box opens. The Variable name field is automatically populated with the name of the data item. | :The Save dialog box opens. The Variable name field is automatically populated with the name of the data item. | ||
''Save dialog box'' | :''Save dialog box'' | ||
[[Image:Save_dialogbox_ToFileshowing.png|291x206px]] | ::[[Image:Save_dialogbox_ToFileshowing.png|291x206px]] | ||
:: | |||
{| | {| | ||
|- | |- valign="top" | ||
|2. | |2. | ||
| Line 110: | Line 103: | ||
|} | |} | ||
{| style="margin-left:18pt" | |||
{| | |||
|- | |- valign="top" | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 121: | Line 112: | ||
|} | |} | ||
{| style="margin-left:18pt" | |||
{| | |||
|- | |- valign="top" | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 134: | Line 123: | ||
====Dragging and dropping items==== | ====Dragging and dropping items==== | ||
{| | {| | ||
|- | |- valign="top" | ||
| | | | ||
* You can drag a data icon to a shortcut icon to open the Analysis window and analyze the data. | * You can drag a data icon to a shortcut icon to open the Analysis window and analyze the data. | ||
|- | |} | ||
{| | |||
|- valign="top" | |||
| | | | ||
* You can drag a model icon to an shortcut icon to open the Analysis window to load a model, and optionally, apply it to new data. | * You can drag a model icon to an shortcut icon to open the Analysis window to load a model, and optionally, apply it to new data. | ||
|- | |} | ||
{| | |||
|- valign="top" | |||
| | | | ||
| Line 153: | Line 150: | ||
|} | |} | ||
Note: You cannot join data items that do not match in at least one dimension. | '''Note:''' You cannot join data items that do not match in at least one dimension. | ||
Consider the following: | Consider the following: | ||
{| | {| | ||
|- | |- valign="top" | ||
| | | | ||
* DataSet item: A, 300 rows x 20 cols | * DataSet item: A, 300 rows x 20 cols | ||
|- | |} | ||
{| | |||
|- valign="top" | |||
| | | | ||
* DataSet item: B, 200 rows x 20 cols | * DataSet item: B, 200 rows x 20 cols | ||
|- | |} | ||
{| | |||
|- valign="top" | |||
| | | | ||
* DataSet item: C, 300 rows x 1 col | * DataSet item: C, 300 rows x 1 col | ||
|- | |} | ||
{| | |||
|- valign="top" | |||
| | | | ||
| Line 183: | Line 192: | ||
You can join A with B because these DataSets have the same number of columns, or you can join A with C because these DataSets have the same number of rows. For example, when you join A with B, you are given two options: | You can join A with B because these DataSets have the same number of columns, or you can join A with C because these DataSets have the same number of rows. For example, when you join A with B, you are given two options: | ||
''Overwrite existing data dialog box'' | :''Overwrite existing data dialog box'' | ||
[[Image:Overwrite_Existing_Data_dialogbox.png|302x87px]] | ::[[Image:Overwrite_Existing_Data_dialogbox.png|302x87px]] | ||
:: | |||
You can overwrite A with the B data, or you can add the B data to A. In this case, the data is automatically joined as additional rows, and a 500 row x 20 column dataset is created. Similarly, if you join A with C, you can overwrite A with the C data, or you can add the C data to A. In this case, the data is automatically joined as additional columns, and a 300 row x 21 column dataset is created. | You can overwrite A with the B data, or you can add the B data to A. In this case, the data is automatically joined as additional rows, and a 500 row x 20 column dataset is created. Similarly, if you join A with C, you can overwrite A with the C data, or you can add the C data to A. In this case, the data is automatically joined as additional columns, and a 300 row x 21 column dataset is created. | ||
| Line 191: | Line 201: | ||
You can also join A with A_copy because these two data items are identical. You are again given two options for joining the data: | You can also join A with A_copy because these two data items are identical. You are again given two options for joining the data: | ||
''Overwrite existing data dialog box'' | :''Overwrite existing data dialog box'' | ||
[[Image:Overwrite_Existing_Data_dialogbox.png|302x87px]] | ::[[Image:Overwrite_Existing_Data_dialogbox.png|302x87px]] | ||
:: | |||
You can overwrite A with the A_copy data, or you can add the A_copy data to A. If you choose to add the A_copy data to A, you have three options for joining the data: | You can overwrite A with the A_copy data, or you can add the A_copy data to A. If you choose to add the A_copy data to A, you have three options for joining the data: | ||
''Augment data dialog box'' | :''Augment data dialog box'' | ||
[[Image:Augment_Data_dialog_box.png|254x87px]] | ::[[Image:Augment_Data_dialog_box.png|254x87px]] | ||
:: | |||
{| | {| | ||
|- | |- valign="top" | ||
| | | | ||
* You can join the data by rows. In this case, a 600 row x 20 column DataSet is created. The 300 new rows are considered as new samples. | * You can join the data by rows. In this case, a 600 row x 20 column DataSet is created. The 300 new rows are considered as new samples. | ||
|- | |} | ||
{| | |||
|- valign="top" | |||
| | | | ||
* You can join the data by columns. In this case, a 300 row x 40 column DataSet is created. The 20 new columns are considered as new variables for the same samples. | * You can join the data by columns. In this case, a 300 row x 40 column DataSet is created. The 20 new columns are considered as new variables for the same samples. | ||
|- | |} | ||
{| | |||
|- valign="top" | |||
| | | | ||
Latest revision as of 14:35, 13 July 2011
Table of Contents | Previous | Next
Manipulating items
After you have imported or loaded data items into the Workspace Browser, a variety of options are available for manipulating the item, including:
- Viewing information about the item
- Opening the item for viewing or editing
- Dragging and dropping items
Viewing information about the item
You can right-click on an icon and on the context menu that opens, select from options for viewing information about the item, renaming the item, and viewing details about the item. For a data item, options are also available for plotting the imported data, editing the item, and analyzing the data. In addition, if multiple data items are selected, then an option to combine the data items is also available.
- Context menu for an item in the Workspace Browser
Opening the item for viewing or editing
Double-click an icon to open the item for viewing only or for editing.
|
- Information dialog box
|
- DataSet Editor window
|
- Open Item dialog box
Because, in general, any data that is loaded into Solo must ultimately be converted to a DataSet object, you can click Create Dataset to proactively carry out this conversion; otherwise, you can click As Raw Data to edit the item "as is." The same window opens whether you click Create DataSet or As Raw Data; however, as shown in the figure below, if you click Create DataSet, all of the tabs are enabled for the Dataset Editor window while if you click As Raw Data, only the Data tab is open for the Data Editor window.
- DataSet Editor window and Data Editor window
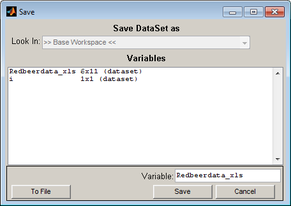
With some exceptions, if you edit a data item, you must explicitly request to overwrite the data item in the Workspace Browser with the changes. To save changes to a data item:
| 1. | In the appropriate Editor window, edit the item as needed, and then on the Editor window menu, click File > Save. |
- The Save dialog box opens. The Variable name field is automatically populated with the name of the data item.
- Save dialog box
| 2. | Do one of the following: |
|
|
Dragging and dropping items
|
|
|
Note: You cannot join data items that do not match in at least one dimension.
Consider the following:
|
|
|
|
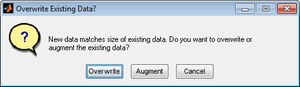
You can join A with B because these DataSets have the same number of columns, or you can join A with C because these DataSets have the same number of rows. For example, when you join A with B, you are given two options:
- Overwrite existing data dialog box
You can overwrite A with the B data, or you can add the B data to A. In this case, the data is automatically joined as additional rows, and a 500 row x 20 column dataset is created. Similarly, if you join A with C, you can overwrite A with the C data, or you can add the C data to A. In this case, the data is automatically joined as additional columns, and a 300 row x 21 column dataset is created.
You can also join A with A_copy because these two data items are identical. You are again given two options for joining the data:
- Overwrite existing data dialog box
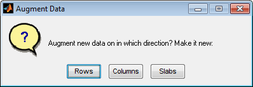
You can overwrite A with the A_copy data, or you can add the A_copy data to A. If you choose to add the A_copy data to A, you have three options for joining the data:
- Augment data dialog box
|
|
|