Diviner: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (28 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Diviner== | ==Diviner== | ||
'''Diviner''' is a semi-automated machine learning (Semi-AutoML) tool specifically designed to enhance the development of multivariate | '''Diviner''' is a semi-automated machine learning (Semi-AutoML) tool specifically designed to enhance the development of linear multivariate regression models. Unlike traditional AutoML systems that entirely automate the machine learning workflow —often sacrificing domain-specific insights and transparency— Diviner strikes a balance between automation and expert involvement. It allows users to efficiently leverage automation while retaining control over critical decision points in the modeling process. This hybrid approach addresses key shortcomings of AutoML, such as the lack of domain knowledge, overfitting, and limited customization, by incorporating user input to guide model development more effectively. | ||
Diviner is a tool designed for calibrating linear models, specifically Partial Least Squares ('''PLS''') and regularized multiple linear regression ('''MLR''') models, such as Elastic Net. It provides a comprehensive workflow that includes outlier assessment, a grid search for preprocessing methods, variable selection, and user-guided model refinement. | Diviner is a tool designed for calibrating linear models, specifically Partial Least Squares ('''PLS''') and regularized multiple linear regression ('''MLR''') models, such as Elastic Net. It provides a comprehensive workflow that includes outlier assessment, a grid search for preprocessing methods, variable selection, and user-guided model refinement. | ||
With its extensive library of preloaded preprocessing methods, Diviner is particularly suited for chemometrics and spectral data analysis. However, users can also create custom preprocessing libraries, making Diviner a versatile tool for linear regression tasks across various data types. | |||
===Data Workflow=== | |||
[[File:Diviner workflow.png|thumb|500px]] | |||
====Exploratory Module==== | |||
'''Data loading:''' The process begins with data being loaded into the system. If a test dataset is available, it should be loaded at this time to evaluate the performance of the models. Note: if a test set is not loaded before the run, applying the models to the test set later will not be possible. | |||
See this page for more information on using the the Diviner Analysis interface: [[Diviner_analysis| Diviner Analysis interface]]. | |||
'''Choice of algorithms:'''PLS is set as the default algorithm, while MLR must be activated in the options. PLS model optimization of number of components (LVs) is included in Diviner's initial grid search. MLR (Elastic Net) performs a separate optimization routine to find the best penalty for each MLR model in the grid search. | |||
[[ | '''Preprocessing:''' This step involves selecting multiple preprocessing methods based on the data type and application. Preprocessing methods for outlier assessment must also be selected at this stage. See this page for more information: [[Diviner_preprocess | Diviner Preprocess interface]]. | ||
=== | '''Cross-validation (CV):''' Diviner supports all cross-validation modes available in the PLS_Toolbox and Solo. This step also sets the number of PLS latent variables (LVs) to be used in the initial grid search. | ||
'''Auto-Variable Selection:''' Variable selection in the initial module uses two fast algorithms: Variable Importance in Projection (VIP) and Selectivity Ratio (sRatio). Learn more about these algorithms [[Selectvars|here]]. | |||
'''Outlier assessment:''' Diviner automatically identifies potential outliers in the dataset using a combination of robust PCA and PLS with the preprocessing methods previously selected by the user. See this page for more information: [[Diviner_review_outliers | review outliers from Diviner]]. | |||
'''Preliminary Output & First Model Selection:''' After the full grid search of PLS (and MLR) models—based on preprocessing recipes, variable selection, and Latent Variable combinations—the initial output is generated as a plot of Overfit (RMSECV/RMSEC) vs. RMSECV. The user manually selects the best models from this plot for refinement or further analysis. See this page for more information: [[Diviner_review_results | review Diviner results]]. | |||
====Refinement Module==== | |||
'''Refinement Process:''' This involves further variable selection and outlier reinclusion. Given that these procedures are time-consuming and not ideal for a large number of models, they are performed only on the models selected from the initial grid search. | |||
'''Further Variable Selection:''' Additional refinement of variable selection is conducted using interval Partial Least Squares (iPLS) to fine-tune which variables contribute to the model. | |||
'''Outlier Reinclusion:''' If any previously excluded outliers are found to be significant upon further analysis, they may be re-evaluated and potentially reintegrated into the models. | |||
'''Final Model Selection and Output:''' After all refinements are completed, the user selects the best-performing models for the final output. | |||
==Command Line Function diviner.m== | |||
===Synopsis=== | |||
diviner - Launches the diviner interface | |||
[allresults] = diviner(x,y,options); | |||
[allresults] = diviner(x_cal,y_cal,x_val,y_val,options); | |||
====Inputs==== | |||
x = X-block (predictor calibration/training block) class "double" or "dataset" | |||
y = Y-block (predicted calibration/training block) class "double" or "dataset" | |||
x_cal = X-block (predictor calibration/training block) class "double" or "dataset" | |||
y_cal = Y-block (predicted calibration/training block) class "double" or "dataset" | |||
x_val = X-block (test/validation block) class "double" or "dataset" | |||
y_val = Y-block (test/validation block) class "double" or "dataset" | |||
options = an optional input options structure | |||
====Output==== | |||
allresults = struct of results | |||
The structure contains the following fields: | |||
* errordata: dataset object with error information for each model in Diviner. This also contains several class sets for the samples. | |||
* errortable: table object containing additional information about each of the Diviner models, such as preprocessing descriptions, and contains the actual models. | |||
* calibrationoutliers: vector of indices from the calibration set the were excluded from calibration. | |||
* preprocesslookup: lookup table for preprocessing classes. | |||
====Optional Inputs==== | |||
options = structure array with the following fields: | |||
* alpha: [ {0.9} ] (1-alpha) measures the number of outliers the algorithm should resist. Any value between 0.5 and 1 may be specified (default = 0.75). Only used when outlier detection is set to 'on'. | |||
* cvi: <nowiki>{{'vet' 5}}</nowiki> Standard cross-validation cell (see crossval) defining a split method, number of splits, and number of iterations. | |||
* preprocessing: {[] []} preprocessing structures or cells for x and y blocks (see PREPROCESS). The first column pertains to the X-block preprocesing, the second column pertains to the Y-block preprocessing. | |||
* outlierdetection: [ {'off'} 'on' ] Governs whether or not to perform outlier detection. | |||
* outlierpreprocessing: {[]} preprocessing structures or cells for x block to use for outlier detection. Only used when outlierdetection is set to 'on'. | |||
* maxlvs: [ {10} ] The maximum number of LVs the PLS models will be built out to. | |||
* exhaustivevarselect: [ {'no'} 'yes' ] Governs the amount of variable selection is done in the first iteration of building PLS models. If 'no', then 'automatic' will be used. If 'yes', then {'automatic', 'iPLS'} will be used. | |||
''' | * savemodels: [ {'yes'} 'no'] Determines whether all of the final models will be saved in the workspace. | ||
* plots: [ 'none' | {'final'} ] governs level of plotting. | |||
* createvalset: [ {'yes'} 'no' ] Determines whether or not the data will be split into a calibration and validation set. This is only 1 X and 1 Y is passed into diviner. | |||
* splitcaltestoptions: options structure from splitcaltest. See splitcaltest. This is only used when createvalset is 'yes'. | |||
== | ===See Also=== | ||
[[browse]], [[preprocess]], [[Diviner_analysis]], [[Diviner_preprocess]], [[Diviner_review_outliers]], [[Diviner_review_results]], [[pls]], [[mlr]] | |||
Latest revision as of 06:26, 26 September 2024
Diviner
Diviner is a semi-automated machine learning (Semi-AutoML) tool specifically designed to enhance the development of linear multivariate regression models. Unlike traditional AutoML systems that entirely automate the machine learning workflow —often sacrificing domain-specific insights and transparency— Diviner strikes a balance between automation and expert involvement. It allows users to efficiently leverage automation while retaining control over critical decision points in the modeling process. This hybrid approach addresses key shortcomings of AutoML, such as the lack of domain knowledge, overfitting, and limited customization, by incorporating user input to guide model development more effectively.
Diviner is a tool designed for calibrating linear models, specifically Partial Least Squares (PLS) and regularized multiple linear regression (MLR) models, such as Elastic Net. It provides a comprehensive workflow that includes outlier assessment, a grid search for preprocessing methods, variable selection, and user-guided model refinement.
With its extensive library of preloaded preprocessing methods, Diviner is particularly suited for chemometrics and spectral data analysis. However, users can also create custom preprocessing libraries, making Diviner a versatile tool for linear regression tasks across various data types.
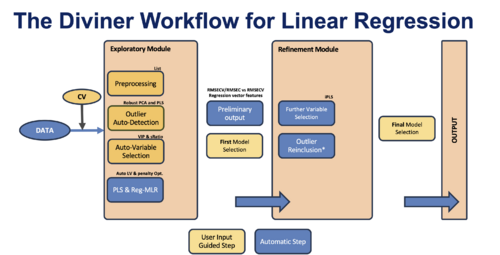
Data Workflow
Exploratory Module
Data loading: The process begins with data being loaded into the system. If a test dataset is available, it should be loaded at this time to evaluate the performance of the models. Note: if a test set is not loaded before the run, applying the models to the test set later will not be possible.
See this page for more information on using the the Diviner Analysis interface: Diviner Analysis interface.
Choice of algorithms:PLS is set as the default algorithm, while MLR must be activated in the options. PLS model optimization of number of components (LVs) is included in Diviner's initial grid search. MLR (Elastic Net) performs a separate optimization routine to find the best penalty for each MLR model in the grid search.
Preprocessing: This step involves selecting multiple preprocessing methods based on the data type and application. Preprocessing methods for outlier assessment must also be selected at this stage. See this page for more information: Diviner Preprocess interface.
Cross-validation (CV): Diviner supports all cross-validation modes available in the PLS_Toolbox and Solo. This step also sets the number of PLS latent variables (LVs) to be used in the initial grid search.
Auto-Variable Selection: Variable selection in the initial module uses two fast algorithms: Variable Importance in Projection (VIP) and Selectivity Ratio (sRatio). Learn more about these algorithms here.
Outlier assessment: Diviner automatically identifies potential outliers in the dataset using a combination of robust PCA and PLS with the preprocessing methods previously selected by the user. See this page for more information: review outliers from Diviner.
Preliminary Output & First Model Selection: After the full grid search of PLS (and MLR) models—based on preprocessing recipes, variable selection, and Latent Variable combinations—the initial output is generated as a plot of Overfit (RMSECV/RMSEC) vs. RMSECV. The user manually selects the best models from this plot for refinement or further analysis. See this page for more information: review Diviner results.
Refinement Module
Refinement Process: This involves further variable selection and outlier reinclusion. Given that these procedures are time-consuming and not ideal for a large number of models, they are performed only on the models selected from the initial grid search.
Further Variable Selection: Additional refinement of variable selection is conducted using interval Partial Least Squares (iPLS) to fine-tune which variables contribute to the model.
Outlier Reinclusion: If any previously excluded outliers are found to be significant upon further analysis, they may be re-evaluated and potentially reintegrated into the models.
Final Model Selection and Output: After all refinements are completed, the user selects the best-performing models for the final output.
Command Line Function diviner.m
Synopsis
diviner - Launches the diviner interface
[allresults] = diviner(x,y,options); [allresults] = diviner(x_cal,y_cal,x_val,y_val,options);
Inputs
x = X-block (predictor calibration/training block) class "double" or "dataset" y = Y-block (predicted calibration/training block) class "double" or "dataset" x_cal = X-block (predictor calibration/training block) class "double" or "dataset" y_cal = Y-block (predicted calibration/training block) class "double" or "dataset" x_val = X-block (test/validation block) class "double" or "dataset" y_val = Y-block (test/validation block) class "double" or "dataset" options = an optional input options structure
Output
allresults = struct of results
The structure contains the following fields:
- errordata: dataset object with error information for each model in Diviner. This also contains several class sets for the samples.
- errortable: table object containing additional information about each of the Diviner models, such as preprocessing descriptions, and contains the actual models.
- calibrationoutliers: vector of indices from the calibration set the were excluded from calibration.
- preprocesslookup: lookup table for preprocessing classes.
Optional Inputs
options = structure array with the following fields:
- alpha: [ {0.9} ] (1-alpha) measures the number of outliers the algorithm should resist. Any value between 0.5 and 1 may be specified (default = 0.75). Only used when outlier detection is set to 'on'.
- cvi: {{'vet' 5}} Standard cross-validation cell (see crossval) defining a split method, number of splits, and number of iterations.
- preprocessing: {[] []} preprocessing structures or cells for x and y blocks (see PREPROCESS). The first column pertains to the X-block preprocesing, the second column pertains to the Y-block preprocessing.
- outlierdetection: [ {'off'} 'on' ] Governs whether or not to perform outlier detection.
- outlierpreprocessing: {[]} preprocessing structures or cells for x block to use for outlier detection. Only used when outlierdetection is set to 'on'.
- maxlvs: [ {10} ] The maximum number of LVs the PLS models will be built out to.
- exhaustivevarselect: [ {'no'} 'yes' ] Governs the amount of variable selection is done in the first iteration of building PLS models. If 'no', then 'automatic' will be used. If 'yes', then {'automatic', 'iPLS'} will be used.
- savemodels: [ {'yes'} 'no'] Determines whether all of the final models will be saved in the workspace.
- plots: [ 'none' | {'final'} ] governs level of plotting.
- createvalset: [ {'yes'} 'no' ] Determines whether or not the data will be split into a calibration and validation set. This is only 1 X and 1 Y is passed into diviner.
- splitcaltestoptions: options structure from splitcaltest. See splitcaltest. This is only used when createvalset is 'yes'.
See Also
browse, preprocess, Diviner_analysis, Diviner_preprocess, Diviner_review_outliers, Diviner_review_results, pls, mlr