Image Preprocessing Methods: Difference between revisions
imported>Donal (→Smooth) |
imported>Donal No edit summary |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
===Dilate=== | ===Dilate=== | ||
Dilation of a binary (0/1, 'off'/'on') image increases the number of 'on' pixels. Consider a pixel's neighboring pixels in a box with side having 'Window' pixels. If the pixel was 'off' but more than the fraction 'Threshold' of the neighboring pixels were 'on' then dilation turns the pixel 'on'. If the pixel was 'on' originally it will not be altered by dilation. | Dilation of a binary (0/1, 'off'/'on') image increases the number of 'on' pixels by expanding the area of clusters of 'on' pixels. Consider a pixel's neighboring pixels in a box with side having 'Window' pixels. If the pixel was 'off' but more than the fraction 'Threshold' of the neighboring pixels were 'on' then dilation turns the pixel 'on'. If the pixel was 'on' originally it will not be altered by dilation. | ||
Parameters: | Parameters: | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
===Erode=== | ===Erode=== | ||
Erosion of a binary (0/1, 'off'/'on') image decreases the number of 'on' pixels. Consider a pixel's neighboring pixels in a box with side having 'Window' pixels. If the pixel was 'on' but more than fraction 'Threshold' of the neighboring pixels were 'off' then erosion turns the pixel 'off'. If the pixel was 'off' originally it will not be altered by erosion. | Erosion of a binary (0/1, 'off'/'on') image decreases the number of 'on' pixels by shrinking the area of clusters of 'on' pixels. Consider a pixel's neighboring pixels in a box with side having 'Window' pixels. If the pixel was 'on' but more than fraction 'Threshold' of the neighboring pixels were 'off' then erosion turns the pixel 'off'. If the pixel was 'off' originally it will not be altered by erosion. | ||
Parameters: | Parameters: | ||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
===Close (Dilate+Erode)=== | ===Close (Dilate+Erode)=== | ||
Perform dilation followed by erosion. This has the effect of smoothing shapes in the binary image and filling small holes within shapes. | Perform dilation followed by erosion. This has the effect of smoothing shapes (clusters of 'on' pixels) in the binary image and filling small holes within shapes. | ||
Parameters: | Parameters: | ||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
===Open (Erode+Dilate)=== | ===Open (Erode+Dilate)=== | ||
Perform erosion followed by dilation. This has the effect of smoothing shapes in the binary image and removing small shapes or isolated pixels. | Perform erosion followed by dilation. This has the effect of smoothing shapes (clusters of 'on' pixels) in the binary image and removing small shapes or isolated pixels. | ||
Parameters: | Parameters: | ||
Revision as of 13:40, 11 March 2012
MIA_Toolbox adds several extra preprocessing methods to the standard set available in the Analysis window's Preprocessing menu choices. These image-specific preprocessing methods are aware of the 2-D image nature of the data and are applied two dimensionally.
Image Preprocessing Methods
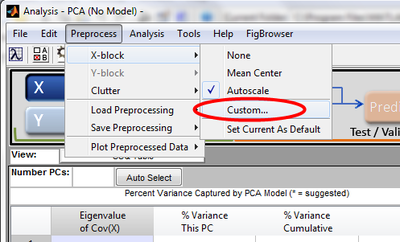
These image preprocessing methods are available from the Analysis menu by selecting "Preprocession" -> "X-block" and choosing "Custom".
which presents the available preprocessing methods. These image preprocessing methods are listed under "Image Filters"
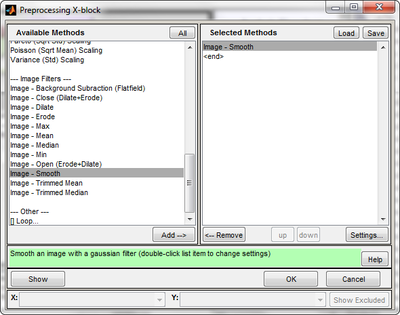
This preprocessing methods window allows you to add selected methods to the X-block preprocessing, and the selected methods are shown in the panel on the right. You can configure available parameters for any of these chosen methods by selecting it and then clicking the "Settings" button which opens a new "Settings" window.
Available Methods
The image analysis preprocessing methods are:
- Smooth: Spatial smoothing for images.
- Background Subtraction (Flatfield): Rolling-ball background subtraction for images.
- Close (Dilate+Erode): Perform dilation followed by erosion on a binary image.
- Dilate: Perform dilation on a binary image.
- Erode: Perform erosion on a binary image.
- Max: Max value over neighboring pixels.
- Median: Median value over neighboring pixels.
- Mean: Mean value over neighboring pixels.
- Min: Min value over neighboring pixels.
- Open (Erode+Dilate): Perform erosion followed by dilation on a binary image.
- Trimmed Mean: Trimmed mean value over neighboring pixels.
- Trimmed Median: Trimmed median value over neighboring pixels.
Method Descriptions
The methods and their configurable parameters are described here:
Smooth
Smoothing of grayscale image by applying convolution with the Gaussian function
Parameters:
- Window: an odd positive integer controlling the width of the Gaussian. Default = 7. Larger values increase smoothing.
Background Subtraction (Flatfield)
Background subtraction subtracts a low-frequency 2D background from a grayscale image using the rolling-ball method implemented in ImageJ's Subtract Background command. The method identifies and removes a background from each slab of an image. The method is applied to each slice of the image in turn. The method involves considering the 2-D grayscale image as a 3-D surface, where height is given by pixel intensity. The surface mapped by the center of a ball as it rolls over the 3-D surface identifies a smoother background surface (after adjusting its height by the ball radius). If 'Light Background' is not enabled, implying a dark background, then the ball would roll along the underside of the 3-D surface. If 'Light Background' is enabled the ball would roll along the upper side of the 3-D surface. The method is based on the concept of the rolling ball algorithm described in Stanley Sternberg's article, "Biomedical Image Processing", IEEE Computer, January 1983. Also see http://imagejdocu.tudor.lu/doku.php?id=gui:process:subtract_background for further details.
Parameters:
- Light Background: A checkbox, disabled by default. Enabled indicates the image has a light background.
- Radius: Specifies the radius of the rolling ball in units of pixels.
Dilate
Dilation of a binary (0/1, 'off'/'on') image increases the number of 'on' pixels by expanding the area of clusters of 'on' pixels. Consider a pixel's neighboring pixels in a box with side having 'Window' pixels. If the pixel was 'off' but more than the fraction 'Threshold' of the neighboring pixels were 'on' then dilation turns the pixel 'on'. If the pixel was 'on' originally it will not be altered by dilation.
Parameters:
- Window: an odd positive integer indicating the size of square window to use. Default = 5. Larger values increase dilation
- Threshold: fraction of an 'off' pixel's neighbors (within window) which must be 'on' to turn that pixel 'on'. Default = 0.1. Increased values inhibit dilation.
Erode
Erosion of a binary (0/1, 'off'/'on') image decreases the number of 'on' pixels by shrinking the area of clusters of 'on' pixels. Consider a pixel's neighboring pixels in a box with side having 'Window' pixels. If the pixel was 'on' but more than fraction 'Threshold' of the neighboring pixels were 'off' then erosion turns the pixel 'off'. If the pixel was 'off' originally it will not be altered by erosion.
Parameters:
- Window: an odd positive integer indicating the size of square window to use. Default = 5. Larger values increase erosion.
- Threshold: fraction of an 'on' pixel's neighbors (within window) which must be 'off' to turn that pixel 'off'. Default = 0.1. Increased values inhibit erosion.
Close (Dilate+Erode)
Perform dilation followed by erosion. This has the effect of smoothing shapes (clusters of 'on' pixels) in the binary image and filling small holes within shapes.
Parameters:
- Window: an odd positive integer indicating the size of square window to use. Default = 5.
- Threshold: fraction of pixel's neighbors (within window) used in the Dilate and Erode operations. Default = 0.1.
Open (Erode+Dilate)
Perform erosion followed by dilation. This has the effect of smoothing shapes (clusters of 'on' pixels) in the binary image and removing small shapes or isolated pixels.
Parameters:
- Window: an odd positive integer indicating the size of square window to use. Default = 5.
- Threshold: fraction of pixel's neighbors (within window) used in the Dilate and Erode operations. Default = 0.1.
Max, Min, Median and Mean
These methods give the max, min, median or mean value over neighboring pixels within a box with sides Window pixels long.
Parameters:
- Window: an odd positive integer indicating the size in pixels of square box to use. Default = 5.
Trimmed Median and Trimmed Mean
These methods give the median or mean value within the Window box where the 5% smallest and 5% largest values are excluded before taking the median or mean.
Parameters:
- Window: an odd positive integer indicating the size in pixels of square box to use. Default = 5.